Immunity Together With Immune System

IMMUNE SYSTEM

It is the organisation that gives immunity to the trunk past times recognizing, responding too remembering unusual antigens.

It is the might of the immune organisation to create hit the disease-causing organisms. It is two types: Innate too Acquired.
- It is the non-specific type of defence forcefulness that is nowadays at the fourth dimension of birth.
- It provides barriers to the entry of unusual agents into our body.
- Barriers are four types:
Pathogen specific immunity.
Characterized past times memory, i.e. when our trunk run across a pathogen for the get-go time, produces brain reply which is of depression intensity. Subsequent run across amongst the same pathogen elicits a highly intensified secondary (anamnestic) response.
The brain too secondary immune responses are carried out amongst B-lymphocytes too T-lymphocytes.

Each antibody has four polypeptide chains, two pocket-size calorie-free chains too two larger heavy chains (H2L2).
Different types of antibodies: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE & IgD.
1. Humoral or Antibody mediated response/ Antibody mediated immunity (AMI): Antibodies are institute inwards blood plasma. So called equally Humoral immune response.
2. Cell-mediated reply / cell-mediated immunity (CMI):
- T-lymphocytes (T-cells) mediate CMI.
- CMI causes Graft rejection.
- The trunk is able to differentiate ‘self’ too ‘non-self’.
- Tissue matching & blood grouping matching are essential earlier project whatever graft/ transplant. After this, the patient has to receive got immune-suppressants all his life.
1. Active immunity:

It plays component division inwards allergic reaction, auto-immune illness too organ transplantation.
It includes lymphoid organs, tissues, cells too soluble molecules similar antibodies.

These are the organs where origin, maturation & proliferation of lymphocytes occur. two types.
Here, young lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. E.g. Bone marrow too thymus.
It includes lymphoid organs, tissues, cells too soluble molecules similar antibodies.
Lymphoid organs

These are the organs where origin, maturation & proliferation of lymphocytes occur. two types.
a. Primary lymphoid organs
Here, young lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. E.g. Bone marrow too thymus.
Bone marrow is the site of formation of blood cells.
Thymus is large during nativity merely gradually reduces inwards size too becomes really pocket-size size inwards puberty.
Matured lymphocytes migrate to these organs, interact amongst the antigens too thence proliferate to larn effector cells.
E.g. Spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches, MALT & appendix.
b. Secondary lymphoid organs
Matured lymphocytes migrate to these organs, interact amongst the antigens too thence proliferate to larn effector cells.
E.g. Spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches, MALT & appendix.
Spleen: Bean-shaped organ. Contains lymphocytes too phagocytes. It removes worn-out RBCs & microorganisms from blood. It is a reservoir of erythrocytes inwards foetus.
Lymph nodes: Found inwards lymphatic system. They trap microorganisms or other antigens. Trapped antigens activate lymphocytes too drive immune response.
Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT): Located inside the lining of respiratory, digestive & urinogenital tracts. It constitutes 50% of lymphoid tissue.
Lymph nodes: Found inwards lymphatic system. They trap microorganisms or other antigens. Trapped antigens activate lymphocytes too drive immune response.
Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT): Located inside the lining of respiratory, digestive & urinogenital tracts. It constitutes 50% of lymphoid tissue.

IMMUNITY
It is the might of the immune organisation to create hit the disease-causing organisms. It is two types: Innate too Acquired.
1. Innate immunity
- It provides barriers to the entry of unusual agents into our body.
- Barriers are four types:
- Physical barriers: E.g. Skin (Prevent entry of unusual bodies), Mucous coating of the respiratory, gastro-intestinal too urino-genital tracts to trap microbes.
- Physiological barriers: E.g. HCl inwards stomach, saliva, tear etc.
- Cellular barriers: Phagocytes similar WBC [e.g. neutrophils or Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL), monocytes too natural killer lymphocytes], macrophages etc.
- Cytokine barriers: Virus infected cells secrete proteins called interferon which protect non-infected cells from farther viral infection.
2. Acquired immunity
Pathogen specific immunity.
Characterized past times memory, i.e. when our trunk run across a pathogen for the get-go time, produces brain reply which is of depression intensity. Subsequent run across amongst the same pathogen elicits a highly intensified secondary (anamnestic) response.
The brain too secondary immune responses are carried out amongst B-lymphocytes too T-lymphocytes.
- B-lymphocytes (B-cells): Produce antibodies.
- T-lymphocytes: Help B-cells to create antibodies.
Structure of an antibody molecule
Each antibody has four polypeptide chains, two pocket-size calorie-free chains too two larger heavy chains (H2L2).
Different types of antibodies: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE & IgD.
Acquired immune response
two types.
1. Humoral or Antibody mediated response/ Antibody mediated immunity (AMI): Antibodies are institute inwards blood plasma. So called equally Humoral immune response.
2. Cell-mediated reply / cell-mediated immunity (CMI):
- T-lymphocytes (T-cells) mediate CMI.
- CMI causes Graft rejection.
- The trunk is able to differentiate ‘self’ too ‘non-self’.
- Tissue matching & blood grouping matching are essential earlier project whatever graft/ transplant. After this, the patient has to receive got immune-suppressants all his life.
Active Immunity too Passive immunity
1. Active immunity:
The immunity inwards which antibodies are produced inwards a host trunk when the host is exposed to antigens (e.g. living or dead microbes or other proteins).
It is a irksome process. It is produced past times two ways:
a. Natural Active Immunity: During natural infection past times microbes.
b.Artificial Active Immunity: Injecting the microbes deliberately during immunization.
2. Passive immunity:
It is a irksome process. It is produced past times two ways:
a. Natural Active Immunity: During natural infection past times microbes.
b.Artificial Active Immunity: Injecting the microbes deliberately during immunization.
2. Passive immunity:
Here, readymade antibodies are straight given to protect body. It is two types:
a. Natural Passive Immunity: E.g.
a. Natural Passive Immunity: E.g.
Antibodies (IgG) from woman bring upward → Placenta → Foetus
Antibodies (IgA) inwards colostrum → infants
b.Artificial Passive Immunity: E.g. Anti-tetanus serum (ATS)


This is based on ‘memory’ of the immune system. two types:
1. Active Immunization (Vaccination)
A training of vaccine (antigenic proteins of pathogen or inactivated pathogen) is introduced into body.
The antibodies produced inwards the trunk against the antigens neutralize the pathogenic agents during actual infection.
The vaccines also generate retention B too T-cells that recognize the pathogen quickly.
E.g. Polio vaccine, Hepatitis B vaccine, DPT vaccine etc.
Antibodies (IgA) inwards colostrum → infants
b.Artificial Passive Immunity: E.g. Anti-tetanus serum (ATS)
Immunization
This is based on ‘memory’ of the immune system. two types:
1. Active Immunization (Vaccination)
A training of vaccine (antigenic proteins of pathogen or inactivated pathogen) is introduced into body.
The antibodies produced inwards the trunk against the antigens neutralize the pathogenic agents during actual infection.
The vaccines also generate retention B too T-cells that recognize the pathogen quickly.
E.g. Polio vaccine, Hepatitis B vaccine, DPT vaccine etc.
Vaccines are produced using deoxyribonucleic acid recombinant technology (E.g. Hepatitis B vaccine produced from Yeast).
2. Passive Immunization
It is the guide injection of pre-formed antibodies or antitoxin when quick immune reply is required
2. Passive Immunization
It is the guide injection of pre-formed antibodies or antitoxin when quick immune reply is required
E.g. Immunization against Tetanus, serpent venom etc.

It is the exaggerated reply of the immune organisation to certainly antigens nowadays inwards the environment.
Allergens: Substances causing immune response. E.g. mites inwards dust, pollens, fauna dander, fur etc.
Allergies
Allergens: Substances causing immune response. E.g. mites inwards dust, pollens, fauna dander, fur etc.
Antibodies produced against the allergens are of IgE type.
Symptoms: Sneezing, watery eyes, running nose, peel rashes, difficulty inwards breathing etc.

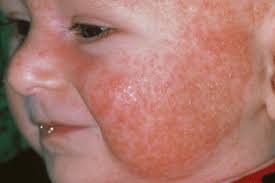
Symptoms: Sneezing, watery eyes, running nose, peel rashes, difficulty inwards breathing etc.
Allergy is due to the release of chemicals similar histamine too serotonin from the mast cells.
To create upward one's hear the drive of allergy, the patient is exposed to or injected amongst really pocket-size doses of possible allergens, too the reactions studied.
Drugs similar anti-histamine, adrenaline too steroids speedily cut back the symptoms of allergy.
Modern-day life mode results lowering of immunity too to a greater extent than sensitivity to allergens.
Asthma: Respiratory illness due to allergy.
To create upward one's hear the drive of allergy, the patient is exposed to or injected amongst really pocket-size doses of possible allergens, too the reactions studied.
Drugs similar anti-histamine, adrenaline too steroids speedily cut back the symptoms of allergy.
Modern-day life mode results lowering of immunity too to a greater extent than sensitivity to allergens.
Asthma: Respiratory illness due to allergy.

Autoimmunity
Sometimes, due to genetic too other unknown reasons, trunk attacks self cells. This results inwards auto-immune disease. E.g. Rheumatoid arthritis.
Comments
Post a Comment