Central Neural Arrangement (Cns) - Encephalon In Addition To Spinal Cord
CENTRAL NEURAL SYSTEM (CNS)
Central neural arrangement consists of 2 parts: Brain as well as Spinal cord
A. BRAIN
Brain has three divisions: Forebrain, Midbrain as well as Hindbrain.
a. Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
Cerebrum
It is the largest part. It has 2 cerebral hemispheres held together past times a thick tissue (Corpus callosum). Each cerebral hemisphere has four lobes. They are Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, Temporal lobe & Occipital lobe. The cerebral cortex (outer portion of cerebrum) has many convulsions (gyri) & depressions (sulci). The gyri growth surface expanse of the cortex to accommodate to a greater extent than neurons. Cerebral cortex is formed of gray matter as well as cerebral medulla (inner region) is formed of white matter.The cerebral cortex consists of the next functional areas:
- Motor area: Controls the voluntary movements of muscles. It is institute inwards the posterior parts of frontal lobe.
- Sensory (Somaesthetic) area: Found inwards parietal lobe (temperature, touch, pressure, pain, gustation etc.), occipital lobe (vision) as well as temporal lobes (hearing & smell).
- Association area: Seen inwards frontal lobe. It is neither clearly sensory nor motor inwards function. Responsible for intersensory associations, retentiveness as well as communication.
Wernicke’s area: Seen inwards temporal lobe. Related amongst agreement spoken language as well as language.
Integrated activities of dissimilar centres of cerebral cortex command intelligence, memory, judgment, learning, thinking as well as articulate speech.
Diencephalon
It includes thalamus as well as Hypothalamus. Ventrally inwards forepart of the diencephalon, the optic nerves crossover as well as fuse to degree the optic chiasma.Thalamus: It acts every bit relay station for sensory as well as motor impulses betwixt cerebrum as well as other parts of the brain.
Hypothalamus:
- Regulates temperature, thirst, hunger as well as emotions.
- Secretes 2 hormones called ADH as well as oxytocin.
- Controls pituitary gland.
- Controls sleep, wakefulness, nutrient intake, blood pressure, pump charge per unit of measurement etc.
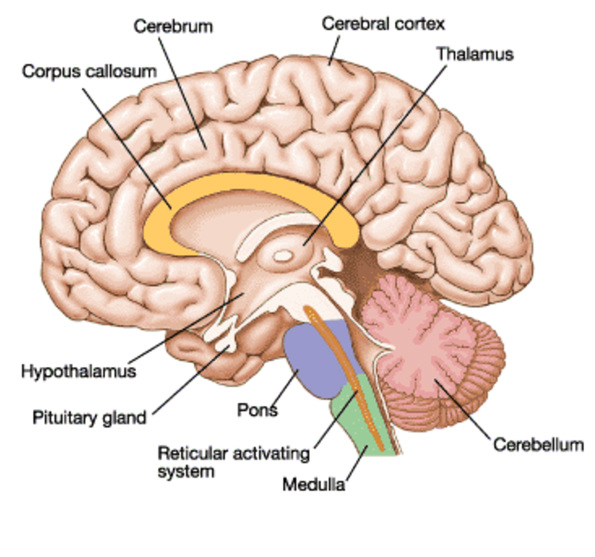
b. Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
It is located betwixt thalamus/hypothalamus as well as Pons. A canal (cerebral aqueduct) passes through the mid brain. Mid encephalon consists of four circular lobes called Corpora quadrigemina. Their anterior duo is the centre of visual reflexes as well as the posterior duo is a centre of auditory reflex.c. Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
It consists of Cerebellum, Pons varoli & Medulla oblongata. Midbrain as well as Hind encephalon together constitute Brain stem.Cerebellum (“little cerebrum”):
Its functions are
- Co-ordination of muscular activities.
- Maintenance of posture as well as equilibrium.
Its functions are
- It is a span betwixt 2 cerebellar hemispheres.
- Co-ordination of the activities of oculus as well as ear.
- Helps inwards equilibration as well as rule of respiration.
Its functions are
Functions:
- Regulation of respiration, heartbeat, blood pressure, circulation, peristaltic movements etc.
- Centre of salivation, vomiting, sneezing & coughing.
B. SPINAL CORD
It is enclosed inside the spinal canal of vertebral column. It is also protected past times meninges. Spinal cord has a primal canal containing CSF. Unlike brain, spinal cord has outer white thing as well as inner greyish matter.Functions:
- Conduction of impulses to as well as from the brain.
- Centre of spinal reflexes.
Comments
Post a Comment